Are you tired of the same old materials? Ready to embrace a future of durability, efficiency, and cost savings? Look no further than aluminum! This versatile metal is revolutionizing construction, offering a range of options tailored to meet the specific needs of your projects.
Cozydoor understands the challenges you face as a construction professional. We’re committed to helping you build stronger, more sustainable projects, while maximizing your budget and minimizing your risks. This comprehensive guide will explore the exciting world of aluminum, providing the knowledge you need to make confident decisions for your next project.
The Properties of Different Aluminum Types
Aluminum is a remarkable material with exceptional versatility. Its unique properties make it a prime choice for a wide range of construction applications.
What Makes Aluminum Unique?
Aluminum stands out due to its exceptional combination of lightweight, corrosion resistance, and conductivity.
- Lightweight: Aluminum is remarkably lightweight, making it ideal for structures where weight reduction is crucial, like roofs, facades, and building enclosures. This translates into easier installation, less stress on foundations, and potential cost savings on transportation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum forms a natural oxide layer that protects it from corrosion, eliminating the need for additional coatings in many applications. This makes it particularly advantageous for outdoor structures, ensuring long-term durability and reducing maintenance costs.
- Conductivity: Aluminum exhibits excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical wiring, heat sinks, and other applications where efficient heat dissipation is essential.
Key Properties that Differentiate Aluminum Types
Beyond its core properties, the specific characteristics of different aluminum types play a significant role in construction.
- Strength: Aluminum alloys can achieve remarkable tensile strength, rivalling steel in some applications. This strength is crucial for structural elements like beams, columns, and framing, ensuring stability and safety.
- Formability: Aluminum exhibits high formability, making it easy to shape and bend into complex geometries. This characteristic is particularly valuable for creating intricate designs for architectural elements, facades, and custom structures.
- Weldability: Aluminum can be easily welded, allowing for seamless connections and efficient assembly of complex structures. This characteristic reduces labor costs and improves project timelines.
The Influence of Alloying Elements on Aluminum’s Properties
The addition of alloying elements, like magnesium, copper, manganese, and silicon, significantly influences the characteristics of aluminum, creating a diverse array of alloys tailored to specific needs.
- Magnesium (Mg): Increases strength and improves weldability, commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Copper (Cu): Enhances strength and electrical conductivity, often found in high-performance structures and electrical applications.
- Manganese (Mn): Improves strength and corrosion resistance, widely used in marine environments and outdoor structures.
- Silicon (Si): Improves castability and wear resistance, commonly found in engine blocks and automotive components.
Exploring Common Aluminum Alloys and their Applications
The aluminum alloy series system, established by the Aluminum Association (AA), provides a convenient way to categorize and identify various aluminum alloys.
Wrought Aluminum Alloys
Wrought aluminum alloys are highly formable, making them ideal for fabrication into various shapes and profiles.
- 1xxx Series: Commercial Purity Aluminum
- This series, featuring a high aluminum content with minimal alloying elements, exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and workability.
- Applications: Building materials, food containers, heat exchangers, and chemical equipment.
- 2xxx Series: Copper Alloys
- The addition of copper to this series enhances strength and heat treatability, resulting in alloys known for their high tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace components, aircraft parts, marine structures, and high-performance automotive parts.
- 3xxx Series: Manganese Alloys
- This series, characterized by its manganese content, offers good strength, weldability, and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Structural components, truck bodies, pressure vessels, and marine applications.
- 5xxx Series: Magnesium Alloys
- Magnesium enhances the strength and weldability of this series, making it a popular choice for applications requiring high strength and durability.
- Applications: Storage tanks, marine components, and structural elements.
- 6xxx Series: Magnesium and Silicon Alloys
- This series combines the strength and weldability benefits of magnesium with the castability and wear resistance of silicon.
- Applications: Architectural structures, windows, doors, and automotive components.
- 7xxx Series: Zinc Alloys
- Zinc, added to this series, significantly enhances strength and heat treatability, resulting in alloys known for their high strength and durability.
- Applications: Aircraft components, rocket parts, and high-performance structural applications.
Cast Aluminum Alloys
Cast aluminum alloys are melted and poured into molds, creating solid shapes for various applications.
- Common Cast Aluminum Alloys and Their Uses:
- 300 Series: Used for general-purpose castings, like housings, brackets, and engine blocks.
- 350 Series: Offers good strength and wear resistance, commonly found in automotive parts and machinery components.
- 380 Series: Known for its high strength and castability, often used in structural components and automotive parts.
Comparing Aluminum with Close Entities
To fully appreciate the unique advantages of aluminum, it’s helpful to compare it with other common construction materials.
Aluminum vs Magnesium
While magnesium is also a lightweight metal, it’s significantly less strong and offers lower corrosion resistance than aluminum. However, magnesium is less expensive than aluminum, making it a viable option for certain applications where cost is a primary concern.
- Weight: Magnesium is lighter than aluminum, offering potential weight savings.
- Strength: Aluminum is generally stronger than magnesium, making it a preferred choice for structural elements.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum offers superior corrosion resistance compared to magnesium, especially in humid environments.
- Cost: Magnesium is less expensive than aluminum, making it attractive for cost-sensitive projects.
Aluminum vs Titanium
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it a top contender for high-performance applications. However, titanium’s high cost often restricts its use to specialized projects.
- Weight: Titanium is heavier than aluminum, potentially affecting structural design.
- Strength: Titanium is significantly stronger than aluminum, ideal for high-stress environments.
- Corrosion Resistance: Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive environments.
- Cost: Titanium is significantly more expensive than aluminum, making it cost-prohibitive for most construction projects.
Aluminum vs Copper
Copper’s high electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it a popular choice for electrical wiring and plumbing applications. However, copper is more expensive and heavier than aluminum, making it less practical for structural applications.
- Weight: Copper is heavier than aluminum, potentially adding to the weight of structures.
- Strength: Aluminum’s strength is comparable to copper, making it a viable option for structural elements.
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments.
- Conductivity: Copper exhibits superior electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for wiring and heat transfer applications.
- Cost: Copper is generally more expensive than aluminum, making it less cost-effective for large construction projects.
Read more Blog & New:
Manufacturing Processes and their Impact on Aluminum Grades
The manufacturing processes used to shape and treat aluminum significantly impact its properties and suitability for specific applications.
Casting Processes for Aluminum
Casting involves melting aluminum and pouring it into molds to create solid shapes.
- Sand Casting: A cost-effective method using sand molds to create intricate shapes for various applications.
- Die Casting: Uses metal molds for high-volume production of complex, intricate shapes, often used in automotive parts and machinery components.
- Permanent Mold Casting: Offers greater dimensional accuracy and smoother surfaces than sand casting, commonly used in engine blocks and pump housings.
Aluminum Extrusion: Shaping the Metal
Extrusion involves forcing aluminum through a die to create specific shapes and profiles.
- Aluminum Extrusion: A highly versatile process that enables the creation of various profiles, including beams, channels, pipes, and custom shapes.
- Benefits of Extrusion: High strength and dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for structural elements, framing, and architectural designs.
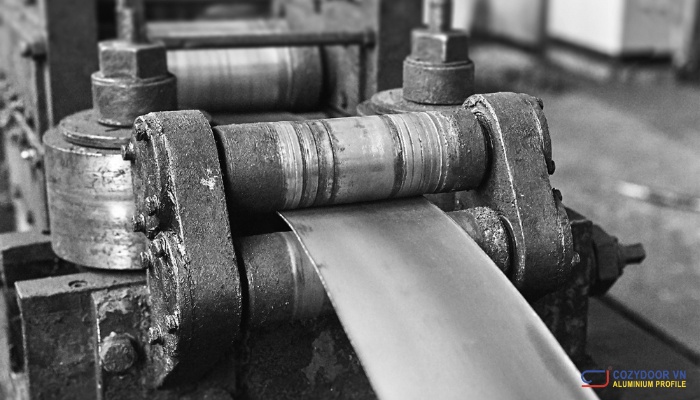
Aluminum Rolling: Creating Sheets and Plates
Rolling involves passing aluminum through rollers to reduce its thickness and create sheets and plates.
- Aluminum Rolling: A common process for creating flat aluminum sheets and plates with precise dimensions.
- Applications: Building facades, roofing, siding, and decorative panels.
Heat Treatment: Enhancing Aluminum’s Properties
Heat treatment involves controlled heating and cooling of aluminum to modify its properties.
- Solution Heat Treatment: Increases strength and ductility.
- Precipitation Hardening: Increases strength and stiffness by forming small precipitates within the aluminum alloy.
- Annealing: Reduces hardness and improves formability.
The Sustainability and Recycling of Aluminum
Aluminum is a highly sustainable material, offering significant environmental benefits throughout its lifecycle.
The Aluminum Recycling Process: A Circular Economy
Aluminum is 100% recyclable, meaning it can be melted down and reused repeatedly without any loss of properties.
- Recycling Process: Scrap aluminum is collected, melted down, and recast into new aluminum products.
- Benefits of Recycling: Reduces the need for mining new aluminum, lowering environmental impact.
Advantages of Using Recycled Aluminum
Choosing recycled aluminum can significantly contribute to sustainable construction practices.
- Energy Savings: Recycling aluminum requires significantly less energy than producing aluminum from raw materials, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Resource Conservation: Recycling aluminum helps conserve natural resources and reduces the environmental impact of mining.
- Cost Savings: Recycled aluminum is often more cost-effective than virgin aluminum, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
Assessing the Environmental Impact of Aluminum
While aluminum production can have environmental implications, its recyclability and overall energy efficiency make it a more sustainable choice compared to many other construction materials.
- Mining Aluminum: Mining bauxite ore, the raw material for aluminum production, can have environmental impacts, including deforestation and soil erosion.
- Aluminum Production: The process of refining bauxite into aluminum requires significant energy and can generate greenhouse gas emissions.
- Aluminum Recycling: Recycling aluminum significantly reduces the energy and environmental impact associated with aluminum production.
At Cozydoor, we’re committed to providing you with the highest quality aluminum products and expert guidance to help you succeed in your construction projects. We understand the complexities of building with aluminum and are here to provide support every step of the way.
Contact us today for a free consultation! Our team of experts will work with you to identify the best aluminum solutions for your specific project needs, ensuring durability, cost-effectiveness, and long-term performance.













Is Aluminum a Metal? Unlocking its Potential for Modern Construction
Aluminum’s remarkable properties have revolutionized industries, and its impact on [...]
Nov
6061-T4 vs T6: Choosing the Best Aluminum for Your Project
Ready to elevate your next industrial construction project? Choosing the [...]
Nov
How Aluminium Recycling Helps Protect Our Environment
As a director or project manager in industrial construction, you’re [...]
Nov
Power of Aluminium Die Casting
Are you a construction professional looking to optimize your projects [...]
Nov
Aluminium Coloring Made Simple: Step-by-Step Instructions
Aluminium is a highly versatile material widely used in industrial [...]
Nov
The Amazing Strength of Aluminum: What You Need to Know
At Cozydoor, we understand the challenges you face in delivering [...]
Nov
Feel the Strength of Magnitude 7 Metals in Action
As a project manager, you understand the responsibility of building [...]
Nov
Discover the Different Types of Aluminum and Their Uses
The right aluminum can elevate your construction to new heights, [...]
Nov